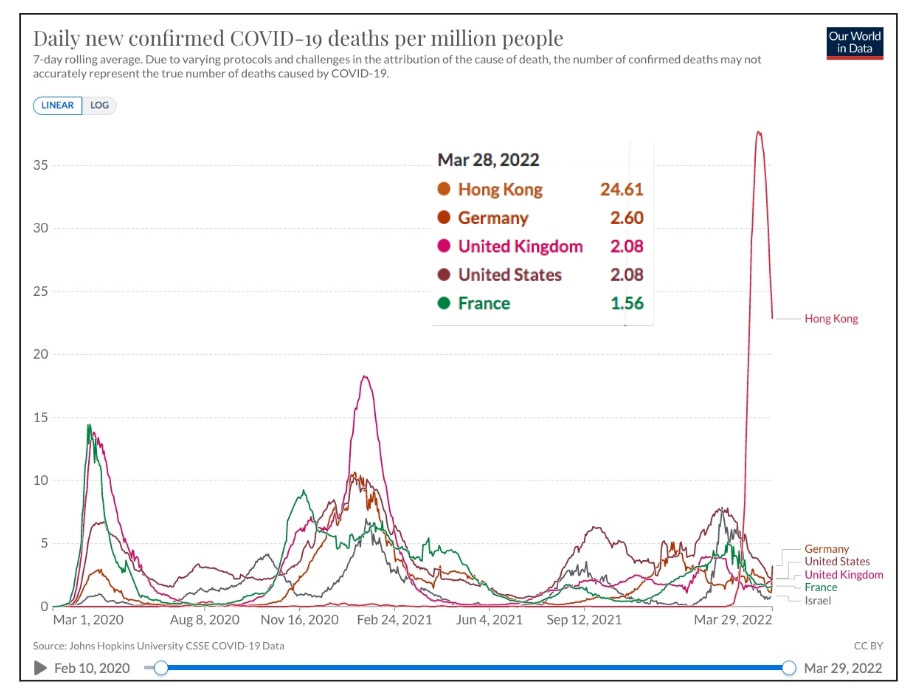
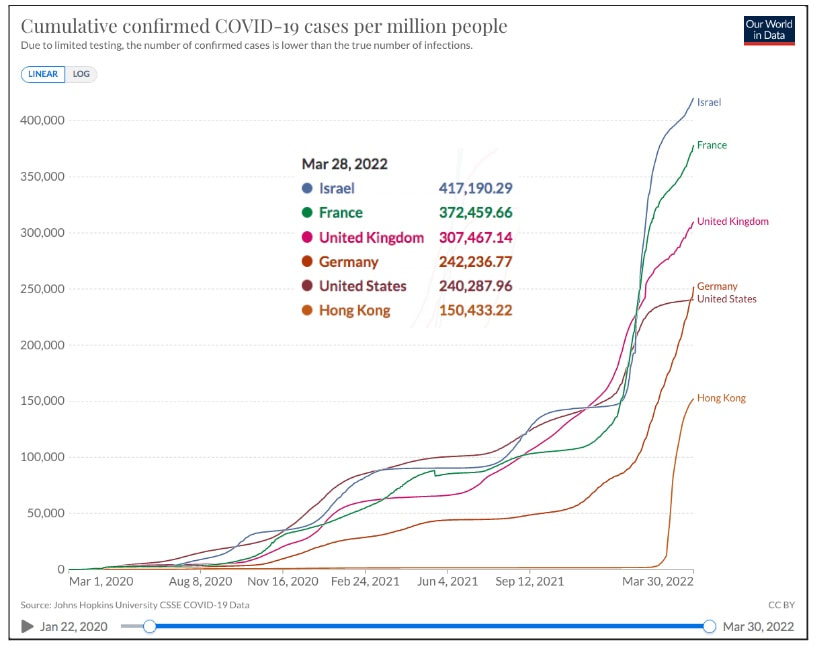
Covid 19 - Down, But Not OutDespite the decision of many countries over the last two months to ease or eliminate COVID restrictions, it is clear that COVID is not over. There are a number of distinct themes:
Concerns:
Refana Update - Proof of Concept on WIV Vaccine Yields Positive Results
Challenge Results
IITRI Paper - American Society of Virology (ASV) Conference - Wisconsin
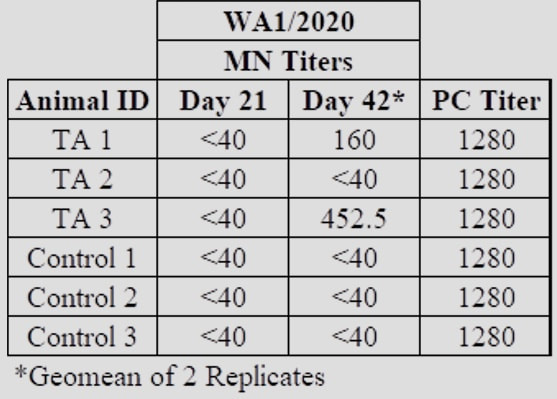
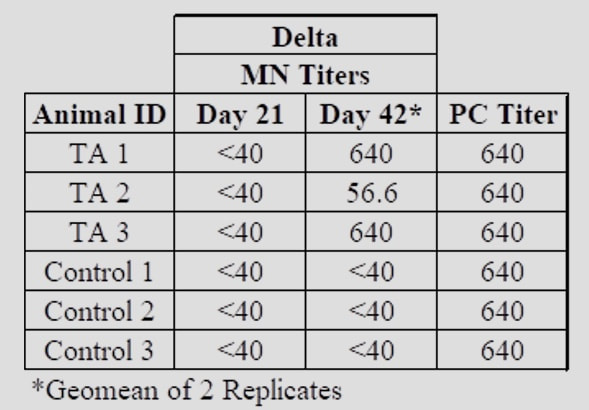
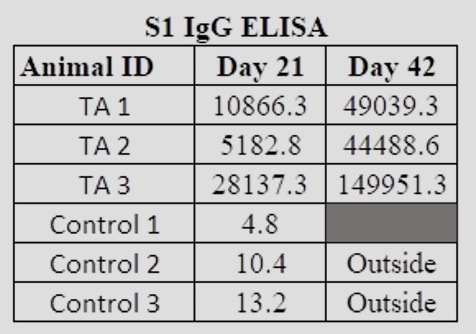
Next StepsRefana is now working with a number of parties on a funding proposal to NIAID, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, for next stages of funding, which would take this project, potentially, to full trials and if successful, ultimate approval Appendix 1Appendix 2Development of a Small Scale Whole Inactivated Vaccine Against B.1.617.2 SARS-CoV-2 Delta Andrew Eaton1, Landon Westfall1, Dianet Giraldo1, Brian Maccaba2, Phillip Schwartz3 and Robert Baker1* 1 Affiliation 1: Division of Microbiology and Molecular Biology, Illinois Institute of Technology Research Institute (IITRI), Chicago, IL 60616 2 Affiliation 2: Refana™, Middletown, DE 19709 3 Affiliation 3: EnteraBio, Jerusalem Israel 9112002 *Correspondence: [email protected] Vaccine development against SARS-CoV-2 variants in humans will be benefited from using multiple types of vaccine constructs. Whole inactivated virus (WIV) vaccines are safe and have been used in the prevention of respiratory viruses such as influenza and polio as well as others, and have the added benefit of more stable storage. Here we have produced, inactivated, purified, and concentrated a Delta B.1.617.2 WIV and tested its efficacy using K18-hACE2 heterozygous mice. We compared varying growth conditions including serum-containing and serum-free medias. Total protein was quantified in both medias with values of 927 µg/mL and 2 µg/mL respectively. Following optimization of conditions, Vero E6 cells were grown in a Corning HyperFLASK® and infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta (B.1.617.2). After harvest, virus was concentrated 500-fold using centrifugal filters and quality controlled at multiple steps using qPCR, Bradford, and SDS-PAGE. The original volume, prior to concentration, had a total SARS-CoV-2 genome content at 1.20E+11 copies. Following 100-fold concentration the total genomes copies was 3.78E+10 which correlates to a ~69% loss during processing. The final vaccine preparation was prepared with a squalene-in-water emulsion adjuvant and tested in K18-hACE2 mice along with shame-vaccinated controls. Mice were prime/boost vaccinated with a total of 0.2 µg and 1.9 µg S1 RBD, respectively. Although vaccinated mice showed only anti-Spike ELISA antibody titers, they showed substantial neutralizing and ELISA titers after boost against both the WA1/2020 and Delta variants (neutralizing titer of approximately 640 post-boost). Protective efficacy of the vaccine was evaluated with a live SARS-CoV-2 Delta challenge. These findings suggest that using a whole inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 should be further evaluated. A whole inactivated vaccine tend to be more temperature stable to reduce transport costs and associated issues to mitigate logistical challenges in delivering to other countries. Key words: Delta B.1.617.2, Whole Inactivated Virus Vaccine, Neutralization titers
0 Comments
|
Practical Solutions for complex and urgent global medical problems
© 2024 Refana Inc


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed